Rosacea: What Lies Beneath the Redness? Causes and Treatment Insights
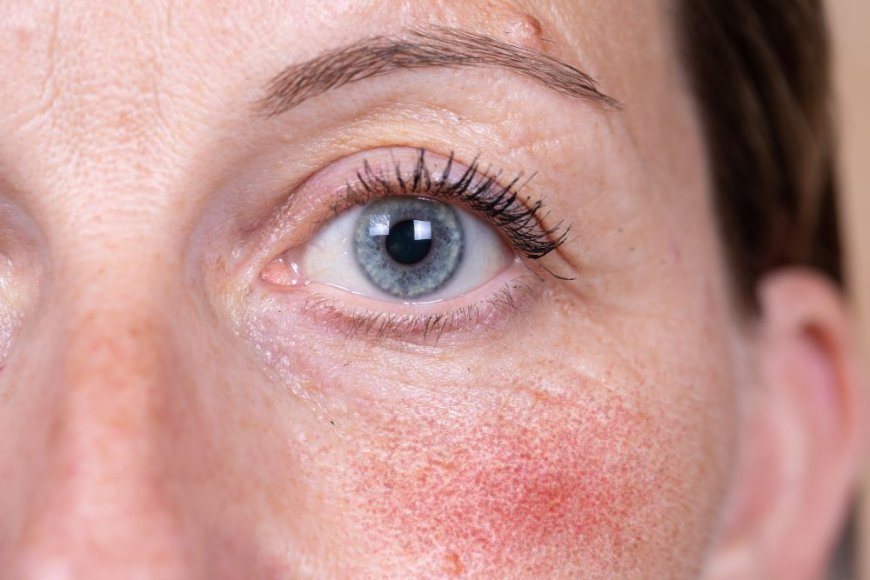
Rosacea is a common yet often misunderstood skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes even pimples, rosacea can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and quality of life. While the cause of rosacea remains unclear, researchers have made strides in understanding its triggers and developing effective treatments. In this article, we will delve into the underlying causes of Rosacea Treatment in Dubai, explore its symptoms, and examine the latest treatment options available.
Understanding Rosacea
Rosacea primarily affects the central part of the face, including the cheeks, nose, and forehead. It is most commonly diagnosed in individuals with fair skin, particularly those aged between 30 and 50. The condition can manifest in various ways, including:
- Erythema: Persistent redness in the face.
- Telangiectasia: Small, visible blood vessels on the surface of the skin.
- Papules and Pustules: Small, red bumps or pimples that may resemble acne.
- Thickened Skin: In more severe cases, the skin may thicken, particularly around the nose, leading to a condition known as rhinophyma.
What Causes Rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea remains unknown; however, several factors have been identified as potential triggers and contributors to the condition:
1. Genetics
There is a strong genetic component to rosacea. Individuals with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it themselves. Studies suggest that certain genetic markers may predispose individuals to rosacea, although further research is needed to fully understand this relationship.
2. Immune System Dysfunction
Emerging research indicates that rosacea may be linked to an abnormal immune response. Individuals with rosacea often show elevated levels of certain inflammatory proteins, suggesting that an overactive immune system may contribute to the condition.
3. Demodex Mites
Demodex mites are tiny organisms that naturally inhabit human skin. Some studies suggest that people with rosacea may have higher populations of these mites, which can lead to inflammation and exacerbation of symptoms. However, the exact role of Demodex in rosacea remains a subject of ongoing investigation.
4. Environmental Factors
Several environmental triggers can provoke rosacea flare-ups. Common triggers include:
- Sun exposure: UV rays can irritate the skin and lead to redness.
- Hot weather: Heat can cause blood vessels to dilate, worsening redness.
- Alcohol consumption: Certain alcoholic beverages, particularly red wine, can trigger flushing.
- Spicy foods: Spices can increase blood flow to the skin and provoke symptoms.
- Emotional stress: Anxiety and stress can also lead to flare-ups.
5. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can play a role in rosacea. Many women report worsening symptoms during menstruation or menopause, suggesting that hormonal changes may trigger or exacerbate the condition.
Treatment Options for Rosacea
While there is currently no cure for rosacea, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve skin appearance. Treatment plans should be tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and triggers. Here are some common approaches:
1. Topical Treatments
Topical medications are often the first line of defense against rosacea. Some commonly prescribed options include:
- Metronidazole: An antibiotic that reduces inflammation and redness.
- Azelaic Acid: Helps to unclog pores and reduce redness.
- Ivermectin: An antiparasitic cream that can reduce inflammation and the presence of Demodex mites.
2. Oral Medications
In more severe cases, healthcare providers may prescribe oral medications, such as:
- Antibiotics: Tetracycline antibiotics like doxycycline can help reduce inflammation and control outbreaks.
- Isotretinoin: In rare cases, this powerful acne medication may be prescribed for severe rosacea that does not respond to other treatments.
3. Laser and Light Therapies
For individuals with persistent redness or visible blood vessels, laser treatments can be effective. Options include:
- Pulsed Dye Laser: Targets and reduces redness by targeting blood vessels in the skin.
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL): Can improve overall skin tone and reduce redness.
4. Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage rosacea symptoms. These may include:
- Sun Protection: Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily.
- Gentle Skin Care: Avoiding harsh products that can irritate the skin and opting for gentle cleansers and moisturizers.
- Identifying Triggers: Keeping a diary of flare-ups can help identify specific triggers, allowing individuals to take preventative measures.
5. Consulting a Dermatologist
If you suspect you have rosacea or are struggling with managing its symptoms, consulting a dermatologist is crucial. A specialist can provide a proper diagnosis and tailor a treatment plan to your specific needs.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a complex skin condition that goes beyond mere redness; it is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune factors. While the condition can be challenging to manage, a range of effective treatments is available to help individuals regain control of their skin and improve their quality of life. By understanding the underlying causes and triggers of rosacea, those affected can take proactive steps towards effective management and treatment, allowing them to face the world with confidence.
